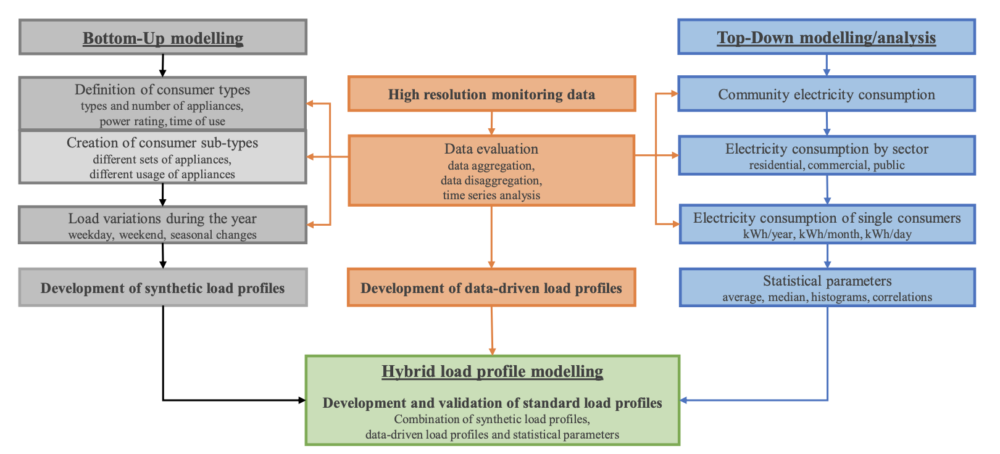
Providing energy access to remote rural communities in sub-Saharan Africa (SSA) is particularly challenging in areas where grid extension is not a viable option. For these communities, electrification and the fulfillment of the UN SDG 7 can only be achieved effectively by using off-grid electricity supply systems. However, the design process of renewable energy-based mini-grids requires a holistic consideration of all electricity needs, including the electricity demand of commercial customers (productive uses) and public institutions. Furthermore, as electric cooking is increasingly becoming a viable option, each off-grid electrification project should carefully consider to which extend electricity can be used for cooking and water heating, and that consumer preferences might change over time when they experience the advantages of e-cooking devices, which can have a profound influence on the resulting electricity load profile and electricity demand. In this research article we explore the advantages of a holistic hybrid modelling approach, which includes bottom-up and top-down modelling as well as data-driven analyses, for the generation of standard load profiles (SLP) for typical consumers in rural off-grid communities in SSA. Monitoring data from the largest off-grid settlement in Namibia, Tsumkwe, is used for data-driven load profile generation as well as for validation within the SLP development process. Finally, the SLP can be added up in order to synthesize customised load profiles for entire off-grid settlements in SSA.
Holistic approach to develop electricity load profiles for rural off- grid
Visited 19 times, 1 visit(s) today